
- Central modules of the ahp decision making how to#
- Central modules of the ahp decision making series#
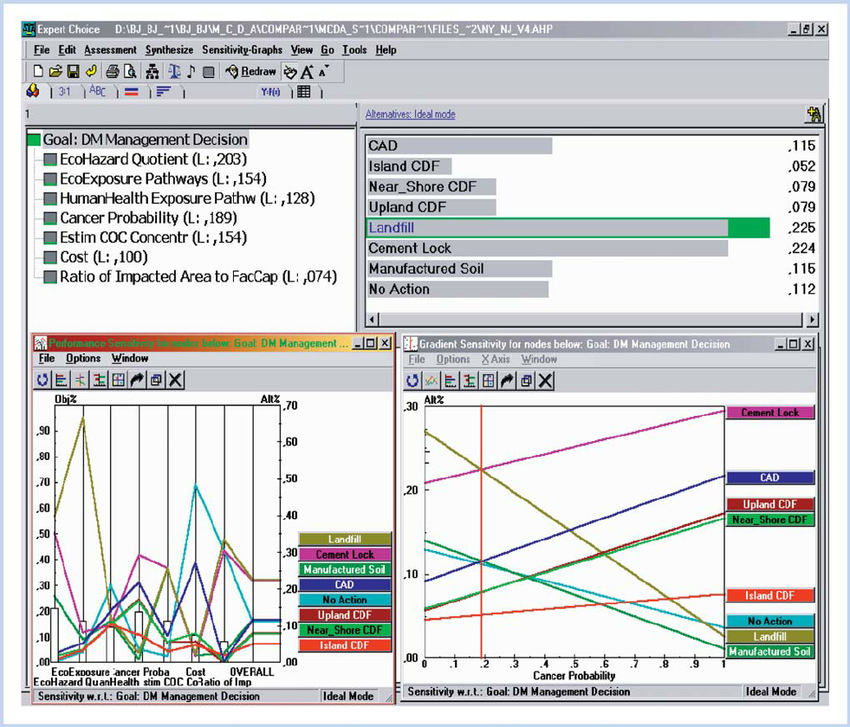
If you add in a D, you then need to compare A-B, A-C, A-D, B-C, B-D, C-D. For example, when comparing options A, B, and C, you would need direct comparisons for A-B, A-C, and B-C. There is an exponentially rising number of comparisons as criteria and options are added. Note that this can be an extremely time-consuming process as the number of criteria and options rises. The tally of all the global scores for each option indicates the best choice. When multiplied out by the weight of the factor, each option is assigned a global score. Similarly, the tally for each decision is broken down so they add up to 1.000. The same rigor is applied to each option for each bottom-level criterion. These factors are shown as a fraction of the decision, with all the factors adding up to 1.000. The scoring of each head to head comparison provides the mathematical basis to assign a weight to that particular bottom-level factor.
Central modules of the ahp decision making series#
This takes complex decisions and breaks them down into a series of small comparisons.
Central modules of the ahp decision making how to#
We will learn how to formulate these problems as mathematical models and solve them using Excel spreadsheet.Essentially, the analytic hierarchy process breaks criteria into progressively smaller criteria, and then compares the criteria at each level in a head to head manner. (c) Manufacturing: What would be the profit maximizing product mix that should be produced, given the raw material availability and customer demand? (c) HR Decisions: How many workers need to be hired or terminated over a planning horizon to minimize cost while meeting operational needs of a company? (b) Production Decisions: Given projected demand, supply of raw materials, and transportation costs, what would be the optimal volume of products to manufacture at different plant locations? (a) Finance Decisions: How should an investment manager create an optimal portfolio that maximizes net returns while not taking too much risks across various investments? Throughout this course we will work on applied problems in different industries, such as:
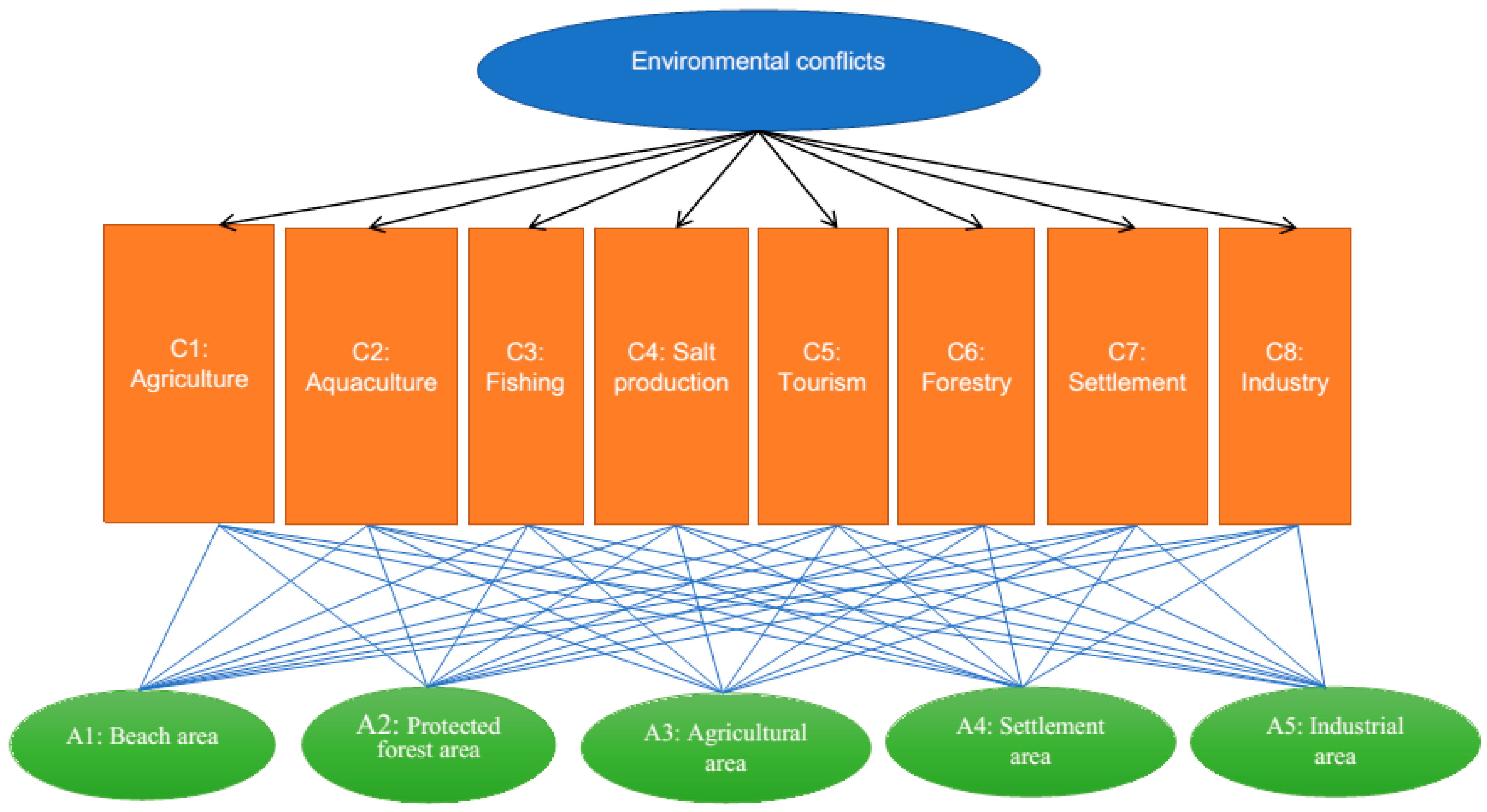
In particular, we understand how linear optimization - a prescriptive analytics method - can be used to formulate decision problems and provide data-based optimal solutions. and the aggregation of individual priorities, traditionally are employed in the Analytic Hierarchy Process to deal with group decision making problems. This course is designed to connect data and models to real world decision-making scenarios in manufacturing, supply chain, finance, human resource management, etc. The use of Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) as a tool is an attempt to identify and include all the parameters which influence the choice of technology. Using the analytic hierarchy process for decision making in engineering applications: some challenges. the AHP module matrix written with Excel was utilized for data analysis. Sixty-two items were retained within 10 domains. Currently, in the countries in the Albanian-speaking regions of the Western Balkans, intuitive decision-making methods predominate. The weights of items were determined employing an analytic hierarchy process (AHP). Managers are therefore interested in acquiring and implementing reliable methods for making decisions both now and in the future. But analytics courses are often focused on training students in data analysis and visualization, not so much in helping them figure out how to take the available data and pair that with the right mathematical model to formulate a solution. Decision making is a significant responsibility for business managers, their decisions impacting business performance. Business analysts need to be able to prescribe optimal solution to problems.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
